Caption
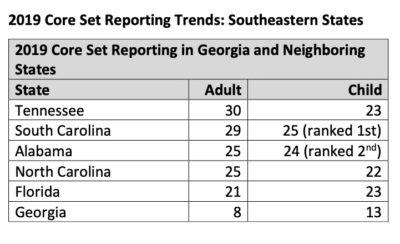
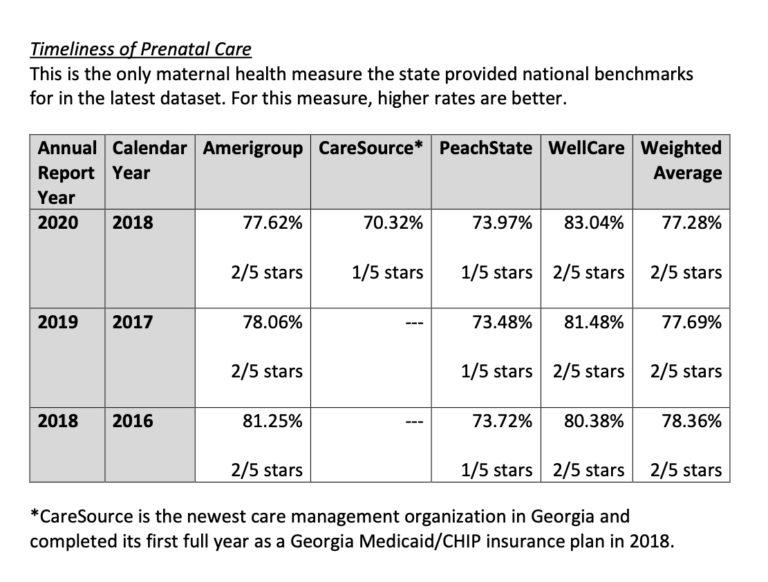
For the past two years, Georgia reported only a fraction of the information the federal Core Set requested. Finding information about how state insurance plans provide care to people with diabetes is also more difficult this year.
Credit: Pexels/Stock photo