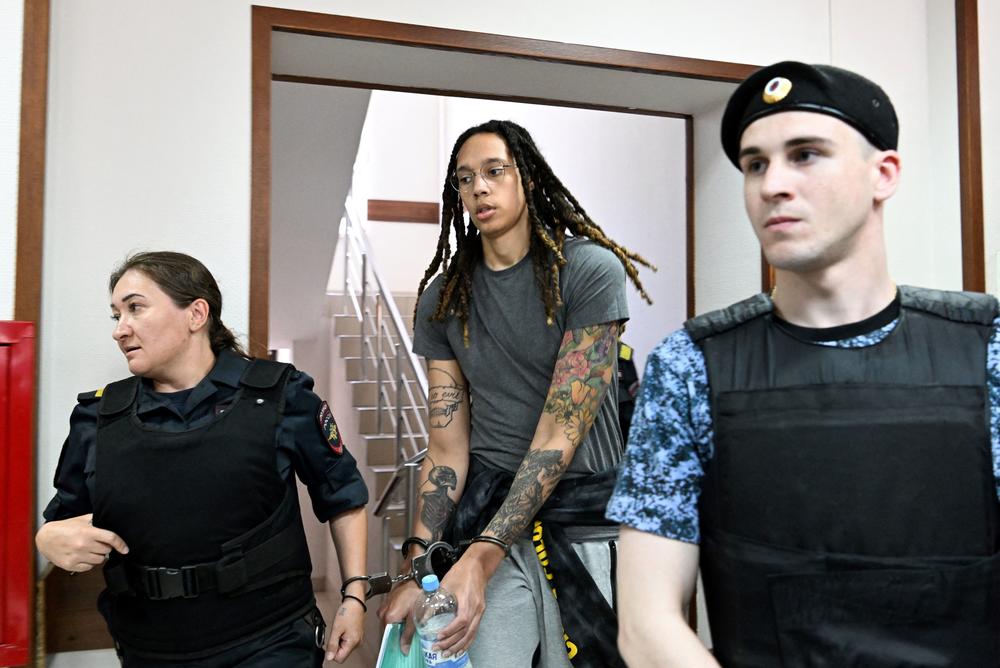Section Branding
Header Content
A Pussy Riot member describes what Brittney Griner can expect in Russian penal colony
Primary Content
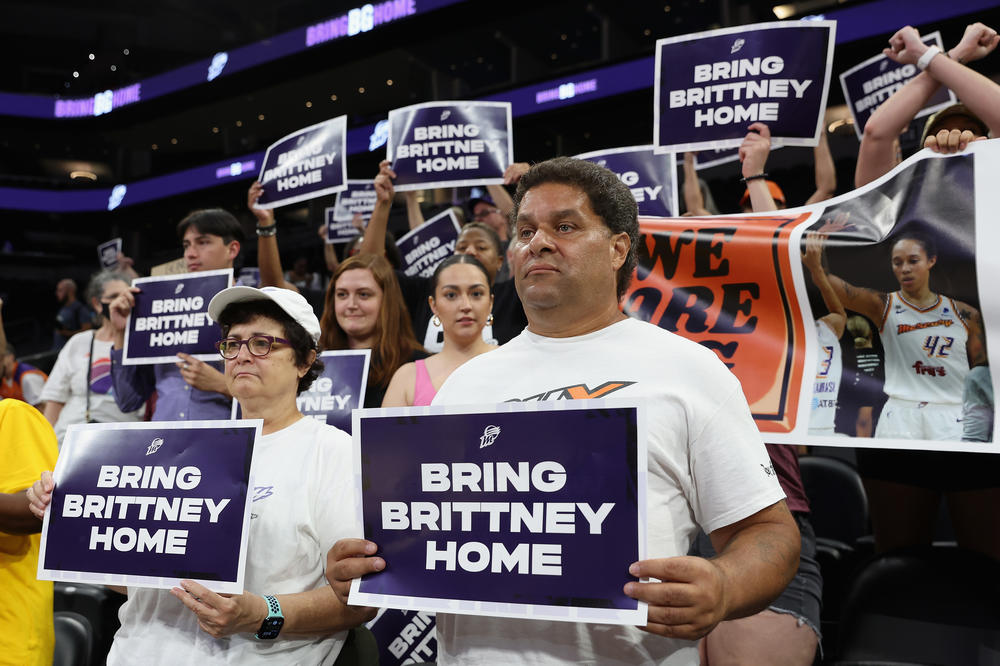
MOSCOW — This week, lawyers for jailed American basketball star Brittney Griner revealed she is currently on her way to a Russian penal colony to begin serving out her nine-year sentence on drug smuggling charges.
Which prison, exactly, is unknown. Neither is Griner's current location. Prisoner transfers often take several weeks, and only then are Russian authorities required to reveal a convict's whereabouts, Griner's legal team says.
Nearly half a million Russians are currently incarcerated— the highest number on the European continent, according to 2022 figures.
Yet those who have spent time in the system say Griner can expect an experience that is more aligned with the Soviet Union's past than most Americans' current ideas of criminal justice.
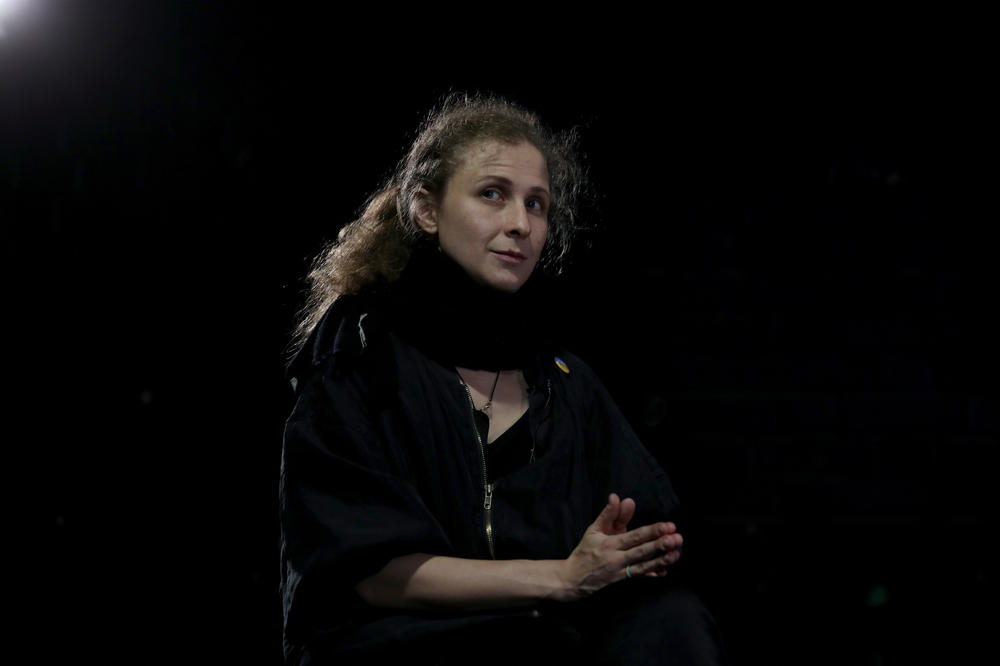
"If jail is possible to imagine, then a penal colony, you can only imagine reading dissidents' books," says Maria Alyokhina, who spent nearly two years in a colony following a protest performance in a Moscow church as a member of the renowned feminist punk collective Pussy Riot.
Alyokhina suggests reading Soviet writers like Alexander Solzhenitsyn, who indelibly captured the grim cruelty of the Soviet camps in his work The Gulag Archipelago.
There's also Alyokhina's own memoir Riot Days, which is also now a traveling live performance of her experiences in a prison colony in the Ural mountains.
"Of course it has a bit better conditions than [the] original gulag system from the 1950s," says Alyokhina, reached by NPR on tour in the United Kingdom. "But the sense is the same. It is a labor camp."
Aloykhina says while most Americans imagine prison cells with bars, Griner can expect to live in "the zone" — a set of barracks with 80 to 100 women sleeping to a room and few, if any, amenities.
"For 100 women, there are like three toilets and no hot water," says Alyokhina. Bathing is a once-a-week occurrence.
Most importantly, she says, in Russian prison colonies, all prisoners must perform forced labor.
"This is a really terrible institution which we received from [the] Soviet Union and it's totally inhuman. The cynical thing is, the work the state provides to the prisoners is sewing uniforms for Russian police and the Russian army," she says.
"This is a legal slavery system. There's nothing about correction or improvement of people's behavior," she adds.
Aloykhina's advice for Griner and her supporters is to keep the pressure on
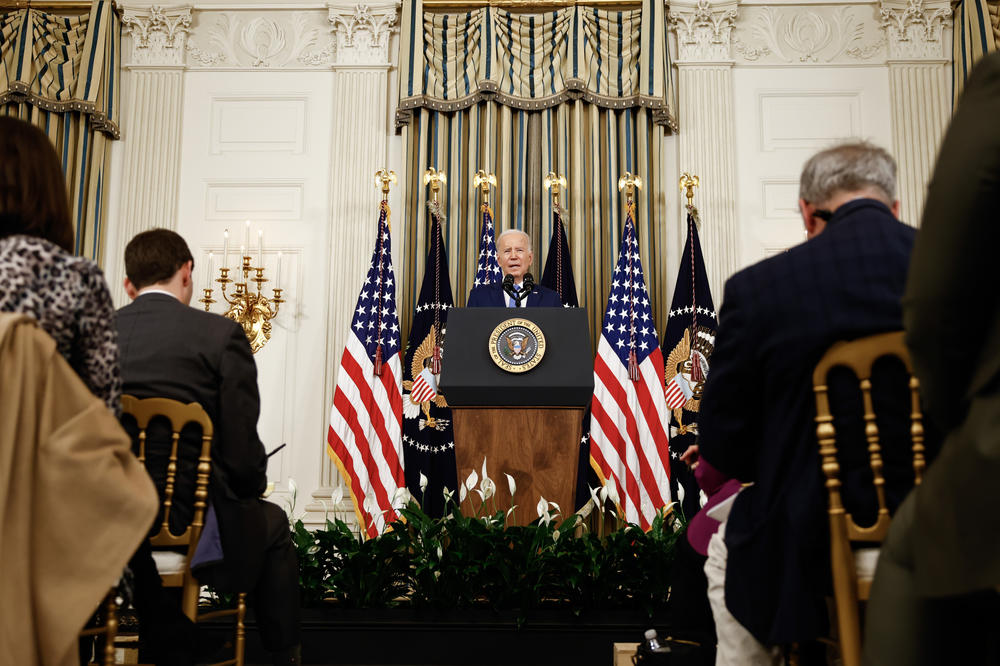
Speaking at the White House on Wednesday, President Biden reaffirmed his desire to reengage the Kremlin in discussions over a potential prisoner exchange.
"My intention is to get her home, and we've had a number of discussions so far, and I'm hopeful that now that our election is over, there's a willingness to negotiate more specifically with us," said Biden. "I am determined to get her home and to get her home safely."
In the meantime, the president has tasked his administration to "prevail on her Russian captors to improve her treatment and the conditions she may be forced to endure in a penal colony," according to administration officials.
But Aloykhina suggests Griner is unlikely to receive special treatment once in the colony.
"It doesn't matter the citizenship of the prisoner," she says.
Asked what advice she would give to Griner, Aloykhina says, "It's important to not forget yourself and not lose your freedom. Because this is what the system teaches you. They teach you how to forget your right to choose."
For Alyokhina, that freedom would come from studying prisoner rights. She levied complaints that eventually led to the dismissal of eight guards for prisoner abuse, she tells NPR.
Together with her bandmate Nadia Tolokonnikova, Alyokhina later founded MediaZona, a news website that covers human rights and prison justice, among other topics.
Alyokhina also offers advice for Griner's family and supporters.
"Write letters. Connect with her lawyers. Ask questions about her inside the system. Do not leave her alone," she says.
"This is what the prisoner administration is telling political prisoners. That they will be forgotten and nobody cares about them," she says.
In Pussy Riot's case, Alyokhina says the constant public attention gave her and her jailed bandmates leverage and power over the prison authorities.
"When they see the person is not forgotten, they start to be much more polite," says Alyokhina.
"This gives hope and protection."
Copyright 2022 NPR. To see more, visit https://www.npr.org.