Section Branding
Header Content
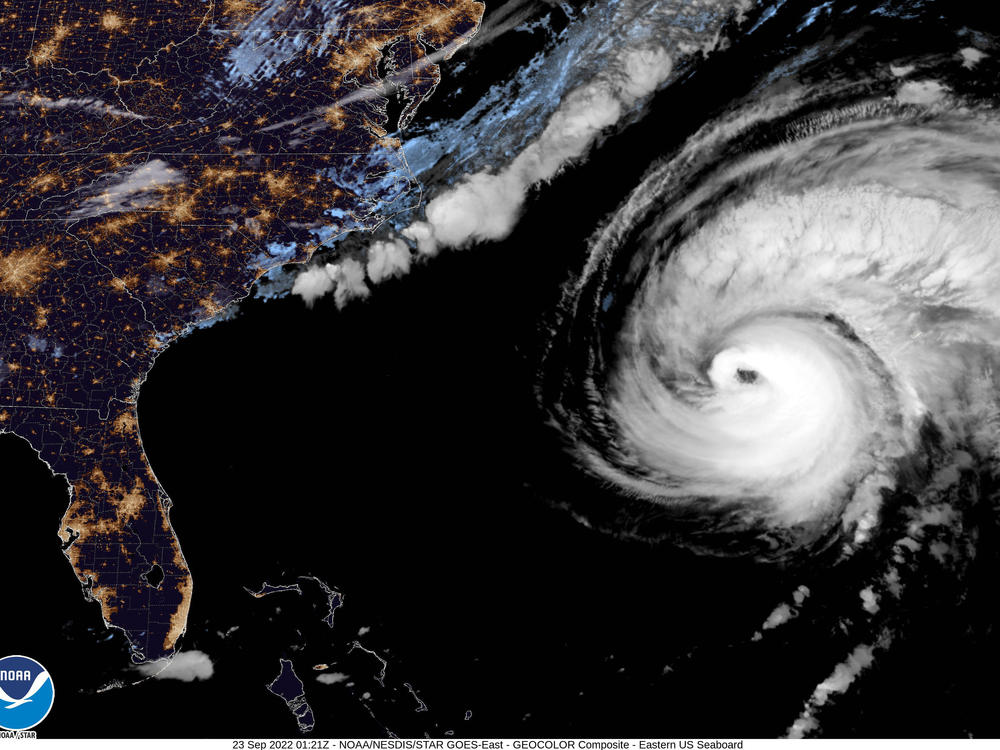
Atlantic hurricane season is now predicted to be 'above-normal' this year, NOAA says
Primary Content
The 2023 Atlantic hurricane season is now projected to have "above-normal level of activity" according to the annual forecast update by scientists at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The above-normal prediction is a change from NOAA's May outlook, which showed that for the first time in eight years, there would be a "near-normal" number of storms.
Earlier in the season, NOAA forecast 12 to 17 named storms. Now the agency projects 14 to 21 storms. The prediction includes tropical storms and hurricanes. About half of those are expected to be full-blown hurricanes. Not all storms make landfall.
"During active years, there's a doubling in the chance of a hurricane hitting the East Coast of the U.S. compared to an average or below-average season," said Matthew Rosencrans, lead hurricane season outlook forecaster, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center.
NOAA says there have been five named storms so far this year. Even though the agency has boosted its activity prediction, the change from May is not unusual. "These changes are well in line with many of the prior outlooks," said Rosencrans.
The main reason scientists expect more activity is that ocean water in areas of the Atlantic Ocean where hurricanes form is abnormally warm right now. It's expected to stay that way throughout hurricane season, which officially started on June 1 and runs through November. That's part of a global trend of rising ocean temperatures due to climate change, although scientists are still trying to understand what is driving this year's record-breaking ocean heat.
"The June/July sea surface temperature in the main development region of the North Atlantic, were the warmest since 1950 at 1.23 degrees centigrade above normal," Rosencrans said.
This is an El Niño year and typically that climate pattern creates wind conditions that disrupt hurricanes. But the warmer water is likely to counterbalance that effect, Rosecrans said.
Federal officials warn people who live in hurricane-prone areas to not focus too much on the total number of storms, because just one storm can cause significant damage.
That means making a plan for how to evacuate if a storm is headed your way, getting ready for power outages and thinking about how to care for elderly family members, people with disabilities, children and pets.
Hurricane risks extend to those who live far from the coast where storms make landfall. Even relatively weak storms can cause dangerous flooding inland, and climate change is making heavy rain from hurricanes more common.
Recently Typhoon Doksuri poured 30 inches of rain on Beijing over five days and left at least 33 people dead in the Chinese capital. Typhoons and hurricanes are the same tropical cyclone weather phenomenon, according to NOAA.
And there are concerns beyond flooding. In Hawaii, strong winds from Hurricane Dora helped wildfires grow on the island of Maui. Residents in the town of Lahaina described harrowing escapes as dozens of buildings were damaged or destroyed. At least 36 people died, officials said.
Copyright 2023 NPR. To see more, visit https://www.npr.org.
Bottom Content